F&O Trading: Everything You Need to Know About Futures and Options

F&O Trading: Everything You Need to Know About Futures and Options
Trading in futures and options represents a sophisticated approach to market participation beyond traditional stock investing. These powerful derivative instruments enable traders to manage risk and pursue profits across diverse market conditions.
What is F&O Trading?
F&O trading encompasses sophisticated financial instruments within the derivatives market. These contracts derive their value from underlying assets including stocks, indices, and commodities. Professional traders utilize futures and options trading for portfolio hedging, price speculation, and generating consistent profits through various trading strategies. Unlike direct equity investment, F&O provides mechanisms to profit from both rising and falling markets. Modern platforms have democratized access to these derivatives, enabling retail traders to trade in F&O and implement sophisticated strategies previously exclusive to institutional investors.
Fundamentals of Futures and Options
Understanding the Basics of Future and Options Trading
Future and options trading involves derivative contracts deriving value from underlying assets. The derivatives market operates through standardized contracts rather than direct asset ownership. These instruments feature specific expiry date and price parameters predetermined in the contract terms.
A futures contract creates obligations for both parties at expiry, while an options contract provides rights without obligations. Professional traders employ these instruments for market speculation and portfolio protection through option trading strategies. The strike price determines execution levels for options, while futures lock in prices for future delivery.
These derivatives function as financial agreements enabling participation in asset price movements without immediate ownership, similar to securing future hotel reservations at current rates.
Key characteristics of derivatives contracts:
- Standardized specifications for exchange trading
- Defined expiry dates (weekly, monthly, quarterly)
- Margin-based trading requiring less capital than spot markets
- Mark-to-market settlement ensuring daily profit/loss adjustment
- Ability to take long or short positions based on market outlook
What Are Futures Contracts?
 Futures contracts establish an obligation to transact at a predetermined price on the expiry date. These binding agreements require margin requirements upfront while providing significant leverage. A Nifty futures contract purchased at 25,000 must be honored at the settlement date regardless of market movement. Exchanges conduct daily mark-to-market settlements, adjusting accounts for gains or losses.
Futures contracts establish an obligation to transact at a predetermined price on the expiry date. These binding agreements require margin requirements upfront while providing significant leverage. A Nifty futures contract purchased at 25,000 must be honored at the settlement date regardless of market movement. Exchanges conduct daily mark-to-market settlements, adjusting accounts for gains or losses.
Steps in executing a futures trade:
- Analyze market direction and select appropriate contract month
- Calculate required initial margin with adequate buffer
- Place order through broker platform specifying contract details
- Monitor position with predetermined stop-loss parameters
- Exit before expiry or roll position to subsequent month
| Aspect | Spot Market Trading | Futures Trading |
|---|---|---|
| Capital Required | Full amount | Margin only (10-20%) |
| Leverage | None available | High leverage provided |
| Settlement | T+2 days | Daily MTM plus expiry |
| Short Selling | Restricted | Freely permitted |
| Holding Period | Unlimited | Until contract expiry |
What Are Options Contracts?
Options contracts grant the right but not obligation to buy or sell an asset at the strike price before expiry. Call options confer rights to buy the underlying asset, while put options provide the right to sell the underlying asset. Buyers pay premiums for this flexibility, representing maximum potential loss. Option writers collect premiums but face potentially unlimited risk.
Contract value comprises intrinsic value (difference between current and expected price) and time value (potential for favorable movement). A call option on major tech stocks at a $1,500 strike costing $30 premium breaks even at $1,530, generating profits above that threshold.
Types of options:
- Call options – Rights to purchase at strike price
- Put options – Rights to sell at strike price
- American options – Exercisable anytime before expiry
- European options – Exercisable only at expiry
Types and Classifications of F&O Instruments
Types of Futures and Options Contracts
Contemporary markets offer diverse futures and options across asset classes. Financial futures encompass stock futures, index futures, and currency derivatives. Commodity futures include gold, crude oil, and agricultural products. The emerging crypto futures market adds Bitcoin futures and cryptocurrency derivatives to traditional offerings. Options classifications include American options (exercisable anytime) and European options (expiry-only exercise).
Asian options utilize average pricing mechanisms. Professional traders select contract types based on prevailing conditions and objectives. Index options provide broad market exposure, while individual stock options enable company-specific strategies. The expanding digital asset derivatives sector introduces perpetual contracts and exotic structures for crypto F&O trading.
| Contract Type | Characteristics | Optimal Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Stock Futures | Individual stock exposure | Directional trades on specific companies |
| Index Options | Broad market coverage | Portfolio hedging, volatility strategies |
| Currency Derivatives | Foreign exchange exposure | Import/export hedging, currency speculation |
| Commodity Futures | Physical goods trading | Inflation hedging, supply/demand plays |
| Crypto Futures | Digital asset exposure | 24/7 trading, high volatility strategies |
Key differences between American, European, and Asian options:
- American – Maximum flexibility with higher premium costs
- European – Lower premiums, suitable for expiry-based strategies
- Asian – Reduced manipulation risk through averaging mechanisms
Capital Market vs Derivatives Market
The capital market and derivatives market serve complementary yet distinct functions. Primary market and secondary market transactions within capital markets involve direct ownership of securities. The derivatives market trades contracts with derived value, facilitating risk management without ownership transfer. Stock exchanges accommodate both markets through different mechanisms. Capital markets focus on price discovery and capital allocation, while derivatives enable risk transfer and leverage utilization. Professional portfolios typically allocate 70-80% to capital markets for core holdings and 20-30% to derivatives for hedging and alpha generation.
F&O Trading Technology and Crypto Innovation
Modern Derivatives Trading Platforms and Innovation
Advanced F&O trading platforms revolutionize derivatives trading technology through AI optimization and sophisticated analytics. Modern trading solutions provide automated analysis of complex Greeks, real-time position monitoring, and comprehensive risk metrics. Integration of crypto derivatives platforms expands opportunities across traditional and digital markets. Risk management systems automatically calculate margin requirements and suggest position adjustments. These technology innovation breakthroughs democratize institutional-grade tools for retail traders.
Upscale.trade exemplifies this revolution in crypto prop trading. We deliver AI optimization specifically engineered for complex derivatives strategies including crypto futures and cryptocurrency options. Unique Telegram integration enables F&O traders to monitor positions and Greeks remotely. Offering up to $100,000 capital access suited for F&O margin requirements across traditional and crypto markets, plus generous 80% profit sharing, Upscale maximizes returns from sophisticated strategies. This represents the future of professional derivatives trading — eliminating traditional barriers while enabling advanced strategy implementation in the evolving crypto derivatives landscape.
Key Differences Between Future and Options
Understanding future and options difference proves crucial for instrument selection. Futures create obligation vs. right — both parties must fulfill contracts at expiry. Options provide flexibility requiring premium payment upfront. Margin requirements differ significantly: futures demand substantial margins maintained throughout, while option buyers risk only premiums.
Risk profiles vary dramatically — futures carry unlimited profit/loss potential, while option buyers face defined maximum loss. Contract obligation in futures means mandatory settlement, whereas option holders can abandon worthless contracts. Leverage operates differently: futures provide direct leverage through margins, while options offer asymmetric payoffs through premiums.
| Feature | Futures | Options |
|---|---|---|
| Obligation | Mandatory for both parties | Right for buyer, obligation for seller |
| Capital Required | Higher margin (15-20%) | Premium only for buyers |
| Profit Potential | Unlimited | Unlimited (calls), Limited (puts) |
| Risk Exposure | Unlimited | Premium for buyers, unlimited for sellers |
| Time Decay | Not applicable | Affects premium value |
Getting Started with F&O Trading
Prerequisites and Account Setup
Initiating F&O trading account setup requires selecting registered brokers offering robust trading platform capabilities. Opening a trading account with F&O segment activation involves submitting income verification meeting regulatory requirements. Completing market research and utilizing educational resources proves essential before active trading. Most brokers provide demo accounts for practice. The progression from account opening to confident trading typically spans 3-6 months of dedicated learning. Traders should start F&O trading with minimal positions, gradually increasing as expertise develops.
Step-by-step process for starting F&O trading:
- Research and select regulated broker with competitive pricing
- Open trading and demat accounts with F&O segment enabled
- Complete risk disclosure documents and income verification
- Fund account with adequate margin for intended trades
- Practice with paper trading for minimum one month
- Begin with single lot trades in liquid contracts
- Gradually scale position sizes as confidence builds
Understanding Margin Requirements and Leverage
Margin requirements constitute the foundation of F&O trading capital efficiency. Initial margin covers potential losses, while maintenance margin ensures position sustainability. SPAN margin calculations determine worst-case scenarios, with exposure margin adding safety buffers.
Margin calls occur when account equity falls below requirements, potentially triggering forced liquidation. Professional traders maintain 150% of required margins as safety reserves. Leverage management involves calculating position sizes relative to total capital, limiting risk to 2% per trade. Trading index futures typically requires approximately $12,000 margin per lot, controlling $120,000 exposure — representing 10x leverage.
Essential F&O Trading Strategies
Basic Strategies for Beginners
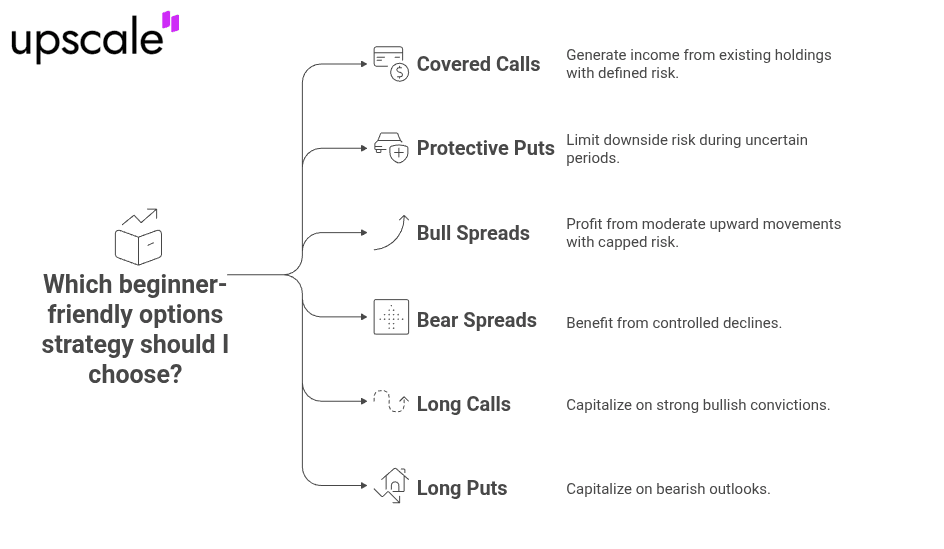
Beginner F&O strategies emphasize simplicity and defined risk parameters. Covered calls generate income from existing holdings through selling call options at higher strikes. Protective puts function as portfolio insurance, limiting downside during uncertain periods. Bull spreads profit from moderate upward movements with capped risk.
Bear spreads benefit from controlled declines. Long call strategies suit strong bullish convictions, while long put positions capitalize on bearish outlooks. Option buying strategy limits losses to premiums paid. Beginners should master buying options before attempting complex strategies. Purchasing technology sector calls at $40 premium risks $2,000 per contract with unlimited upside potential above breakeven.
Advanced Strategies for Experienced Traders
Advanced F&O strategies including iron condor profit from low volatility within defined ranges. Butterfly spread targets specific price levels with limited risk. Calendar spread exploits time decay differences between expiries. Ratio spread adjusts position ratios for skewed risk-reward profiles. Diagonal spread combines different strikes and expiries. Mastering Option Greeks enables delta hedging for market-neutral positions. These strategies require understanding implied volatility, correlation dynamics, and precise execution timing.
Prerequisites before attempting advanced strategies:
- Minimum 12 months successful F&O trading experience
- Complete understanding of Greeks (Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega)
- Ability to calculate position risk across scenarios
- Access to real-time analytics and monitoring tools
| Strategy | Market Condition | Potential Return | Maximum Risk |
|---|---|---|---|
| Iron Condor | Range-bound | 15-25% monthly | Limited to spread width |
| Butterfly | Specific target | 200-300% | Net premium paid |
| Calendar Spread | Stable trend | 30-50% | Net debit paid |
| Ratio Spread | Moderate move | 100-150% | Varies with structure |
Risk Management and Market Analysis
Risk management fundamentally determines long-term F&O success. Professional traders employ strict position sizing rules — allocating a maximum 5% of capital per trade. Stop-loss strategy implementation protects against catastrophic losses. Position sizes follow the 2% rule: with $100,000 capital, maximum loss per trade stays below $2,000. Capital allocation across strategies diversifies risk — 40% to directional trades, 30% to hedging, 30% as reserves. Drawdown management involves reducing position sizes after consecutive losses. Monitoring risk-reward ratio ensures minimum 1:2 favorable outcomes. Portfolio diversification across sectors and expiries prevents concentration risk. Successful traders prioritize capital preservation, understanding profits follow disciplined risk management in F&O trading.
Practical Applications and Market Selection
Stock Selection for F&O Trading
Selecting from the list of future and options stocks requires analyzing liquid options with high open interest. Focus on major index constituents offering tight spreads and substantial trading volume.
Sector selection depends on market cycles — banking during rate changes, technology during earnings seasons. Liquidity ensures smooth entry/exit without slippage. Volatility creates opportunities but demands careful position sizing.
Market capitalization above $50 billion typically ensures adequate derivatives liquidity. Stock futures in major technology and financial companies consistently offer excellent trading conditions. Index futures provide broader exposure with lower stock-specific risk.
F&O Trading in Commodities and Crypto Derivatives
Commodity futures and commodity options offer portfolio diversification beyond equities. Gold trading hedges against inflation, while crude oil futures capture energy sector dynamics. Agricultural commodities follow seasonal patterns. Metals trading tracks industrial demand.
The emerging crypto derivatives trading market introduces Bitcoin futures and Ethereum options with 24/7 availability. Crypto derivatives exchanges offer perpetual contracts unique to digital assets. Cryptocurrency options provide asymmetric exposure to crypto volatility. These markets differ from equity F&O — commodities follow supply/demand fundamentals while crypto F&O trading reflects adoption trends and regulatory developments.
Key differences between equity, commodity, and crypto F&O trading:
- Settlement methods: Equity (cash), Commodity (physical/cash), Crypto (cash/crypto)
- Trading hours: Equity (market hours), Commodity (extended), Crypto (24/7)
- Volatility levels: Equity (moderate), Commodity (seasonal), Crypto (extreme)
- Regulatory framework: Equity (strict), Commodity (moderate), Crypto (evolving)
Common Mistakes and Tax Considerations
Common F&O Trading Mistakes to Avoid
F&O trading mistakes frequently stem from overtrading without clear setups. Improper position sizing amplifies losses beyond recovery capacity. Emotional trading after losses leads to revenge trading and strategy abandonment. Many traders ignore time decay in options, holding positions until worthless expiry.
Trading psychology significantly impacts outcomes — fear and greed destroy disciplined approaches. Risk management failures like avoiding stop-losses create catastrophic drawdowns. Successful traders maintain detailed journals, reviewing mistakes systematically.
Top 10 mistakes made in F&O trading:
- Trading without proper education or practice
- Overleveraging positions beyond risk tolerance
- Ignoring time decay impact on options
- Chasing losses with increased position sizes
- Trading illiquid contracts with wide spreads
- Neglecting margin requirement monitoring
- Holding positions through major events blindly
- Following tips without personal analysis
- Mixing investment and trading capital
- Failing to maintain detailed trade records
Tax Implications and Compliance Requirements
Future and options income tax treatment classifies F&O profits as non-speculative income under business income categories. Tax on derivatives follows regular slab rates rather than capital gains treatment. Traders must file appropriate forms declaring derivative trading as business activity.
Tax audit becomes mandatory when turnover exceeds specified thresholds with profits below minimum percentages. Turnover calculations include absolute values of profits plus losses. Maintaining detailed records including contract notes, margin statements, and P&L reports proves essential. Tax planning through proper expense documentation reduces liability.
Building Your F&O Trading Success Plan
Creating a comprehensive F&O trading plan requires defining clear trading goals aligned with market realities. Realistic targets average 3-5% monthly returns for professional traders. Continuous learning through market analysis, strategy backtesting, and peer discussions enhances skills.
Performance evaluation using metrics like Sharpe ratio identifies improvement areas. Maintaining a disciplined approach following predetermined rules ensures consistency. Successful F&O trading involves consistent execution of edge-positive strategies over time.
Upscale provides ideal environments for implementing sophisticated F&O strategies with professional capital and advanced analytics, allowing traders to focus on strategy execution rather than capital constraints across traditional and emerging crypto derivatives markets.
FAQ
What is the minimum capital required for F&O trading?
Starting F&O trading typically requires $15,000-20,000 for comfortable margin management. Single lot trades in major indices need approximately $12,000 margin, but maintaining buffers prevents forced liquidations during adverse movements.
How do futures contracts differ from options contracts?
Futures contract creates binding obligations for both parties at predetermined price on a future date, requiring margin deposits. Options contracts provide rights without obligations, with buyers paying premiums for flexibility while sellers face potential obligations.
Can beginners start with F&O trading safely?
Beginners can start F&O trading safely through systematic education, paper trading practice, and conservative position sizing. Starting with option buying strategies limits losses to premiums while gaining market knowledge and understanding of market dynamics.
What are the main risks in derivatives trading?
Derivative trading risks associated include leverage amplifying losses, time decay eroding option premiums, and market volatility causing gap movements. Effective risk management through position sizing helps limit potential losses while preserving capital.
How do crypto derivatives compare to traditional F&O instruments?
Crypto derivatives offer 24/7 trading with extreme crypto volatility creating unique opportunities. Bitcoin futures and cryptocurrency options provide exposure to digital assets without custody concerns, though regulatory uncertainty requires additional caution versus traditional F&O contracts.
