Trailing Stop Orders: What They Are and How To Use Them

Mastering Trailing Stop Orders: What They Are and How To Use Them
March 2023. My tech stock surged 27% in two weeks. I watched it drop to 6% overnight. That painful lesson changed everything.
I discovered trailing stop loss orders. They transformed my trading completely. Now I protect profits automatically. My winners run longer. Exits become systematic.
This tool locked in a 19% gain when my crypto position reversed sharply. Without it, profits would have disappeared entirely.
Trailing stops anchor my risk management today. They removed guesswork from exits. They let me sleep during volatile sessions.
Let me show you how they work.
Understanding Trailing Stop Loss: Beyond Basic Risk Management
A trailing stop loss automatically adjusts your exit price as markets move favorably. Unlike regular stops that stay fixed, this dynamic order follows price upward.
Think of it as a rising safety net. Your position climbs higher, protection rises with it. The stop never moves down. It only adjusts upward.
Regular stops protect against losses. Trailing stops lock in accumulated gains while giving trends room to develop.
The key difference: fixed stops sit at one price forever. Trailing stops move up with favorable ticks. This captures extended moves without premature exits.
The beauty lies in automation. Set parameters once. The platform handles everything. No emotional interference needed.
How Trailing Stop Loss Orders Work
Setting a trailing stop requires two decisions. Your initial trigger price. Your trailing distance.
You buy stock at $100. Set 10% trailing stop. Initial stop sits at $90.
Stock rises to $110. Trailing stop adjusts to $99. That's 10% below the new high.
Price climbs to $120. Stop moves to $108. Still maintaining 10% distance.
Reversal comes. Price drops to $109. Stop triggers at $108. Position closes automatically. You captured most of the upward move.
Without trailing, fixed $90 stop stays unchanged. You'd exit with $18 gain instead of $8 loss. That's massive.
Most platforms execute adjustments automatically. You monitor the position. The system handles technical details.
Trailing Stop Loss Example
Let me share a real trade demonstrating this concept.
I entered Ethereum at $1,800 last November. Set 12% trailing stop immediately. Initial stop: $1,584.
ETH rallied to $2,000 in three days. Trailing stop adjusted to $1,760. That's 12% below peak.
Uptrend continued. Price hit $2,200 by week two. Stop moved to $1,936. Profit guaranteed.
Momentum pushed ETH to $2,400 at peak. Trailing stop sat at $2,112. Then reversal began.
Price dropped to $2,150 overnight. Stop triggered at $2,112. Position closed automatically. Final profit: $312 per ETH.
The trailing stop captured 52% of total move. It is protected from reversal. Most importantly, removed emotional decisions.
Try this on demo account first. Test different trailing percentages. Find what matches your risk tolerance.
Types of Trailing Stops
Four main approaches exist for implementing trailing stops. Each serves different trading styles.
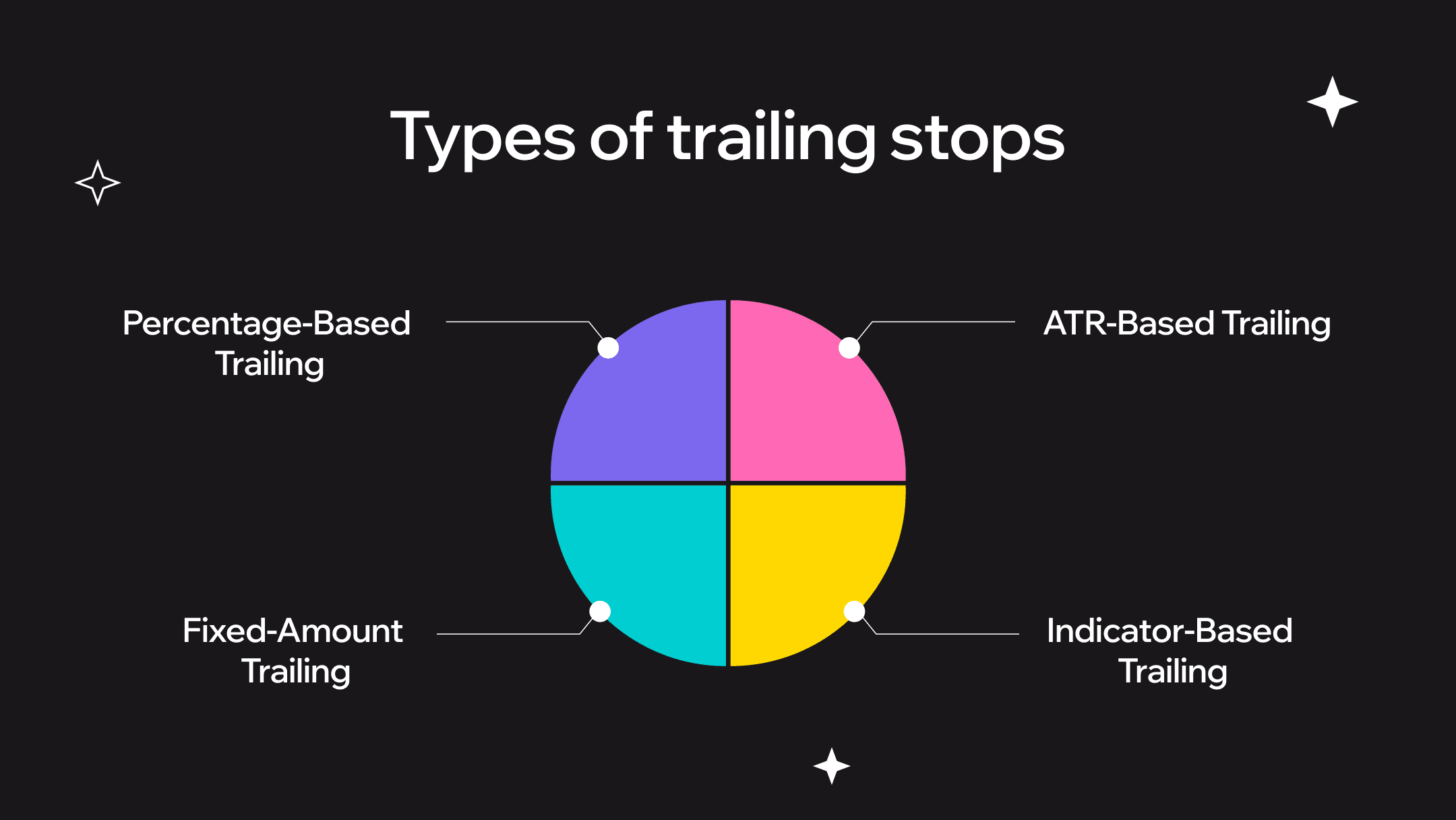 Percentage-Based Trailing
Percentage-Based Trailing
Fixed percentage below current price. Set at 8%, stop trails by that amount consistently.
I use 10-12% for equity positions. Crypto gets 15-18% due to higher volatility.
Best for: Trending markets, long-term positions, less active monitoring.
Fixed-Amount Trailing
Stop follows price by specific dollar amount. Set $5, stop stays $5 below price always.
Works well with lower-priced stocks. Useful for precise risk calculations.
Best for: Day trading, short-term trades, specific risk targets.
ATR-Based Trailing
Uses Average True Range to measure volatility. Set trail at 2-3 times ATR value.
This adapts to changing conditions automatically. High volatility gets wider stops.
I prefer this for swing trades. It respects market character naturally.
Best for: All conditions, volatility-adaptive trading, technical traders.
Indicator-Based Trailing
Use moving averages or support as dynamic stops. The 20-day EMA becomes your trail line.
Price stays above MA, you hold. Price crosses below, you exit.
Best for: Trend followers, technical enthusiasts, longer timeframes.
| Type | Mechanism | Volatility Response | Ideal Timeframe | Complexity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Percentage | Fixed % below price | Manual adjustment | Any | Low |
| Fixed Amount | Fixed $ below price | Manual adjustment | Short-term | Low |
| ATR-Based | Multiple of ATR | Automatic | Medium-term | Moderate |
| Indicator-Based | Follows MA/support | Automatic | Long-term | Moderate |
Match trail type to your strategy. Test individually before combining approaches.
Regular Stop Loss vs. Trailing Stop Loss
The fundamental difference shapes capital protection and profit capture.
Regular Stop Loss
Fixed price trigger. Buy at $50, place stop at $45. That $45 never changes.
Advantages: Precise risk definition, no surprises, perfect for defined targets.
Disadvantages: Misses extended moves, requires manual adjustment, no profit protection.
I use regular stops when trading ranges. Also for positions with specific targets.
Trailing Stop Loss
Adjusts automatically with favorable movement. Stop follows trends upward. Never moves against position.
Advantages: Captures extended moves, locks profits, removes emotion, minimal monitoring.
Disadvantages: Premature exits in choppy markets, more complex, vulnerable to volatility spikes.
My Selection Criteria
Use regular stops when:
- Trading within ranges
- Targeting specific levels
- Making short-term trades
- High-impact news pending
Use trailing stops when:
- Riding established trends
- Profit targets uncertain
- Managing positions passively
- Larger positions need protection
Both tools belong in your arsenal. Regular stops limit losses. Trailing stops maximize gains. Use strategically for different scenarios.
Setting Up Effective Trailing Stop Loss Orders
Implementation varies across platforms. Most brokers support trailing stops through standard interfaces.
Basic Setup Process:
- Access order entry screen after opening position
- Select "Trailing Stop" from order types menu
- Enter trailing percentage or dollar amount
- Review initial stop price and trailing distance
- Activate order to begin automatic tracking
Platform-specific quirks exist. Test on small positions first. Verify execution works as expected.
I manage multiple trailing stops simultaneously. System tracks each position independently. Review adjustments weekly during normal conditions.
OCO Orders
One-Cancels-the-Other combines trailing stops with profit targets. Set both simultaneously. Whichever triggers first closes position.
This hybrid works when trend direction remains uncertain. You capture either profit target or trail stop automatically.
Crypto exchanges like Binance offer similar functionality. Their trailing stops execute 24/7. This continuous protection proves valuable during overnight volatility.
Determining the Optimal Trailing Distance
Finding the right trailing distance balances competing forces. Too tight, normal volatility stops you out. Too wide, you surrender too much profit.
Volatility-Based Method
Calculate current ATR for your instrument. Multiply by 2-3 for trailing distance.
Example: Stock shows ATR of $4. Set trail at $8-12 below price. Wider trails for higher ATR.
I recalculate ATR weekly. Adjust distances when volatility shifts significantly.
Percentage Approach
Use fixed percentages based on volatility ranges:
- Low volatility (blue-chips): 5-7% trailing distance
- Moderate (growth stocks): 8-12%
- High volatility (small-caps, crypto): 13-20%
Timeframe Adjustment
Trading timeframe affects optimal distance:
- Day trading: 3-5% trails
- Swing trading: 8-12%
- Position trading: 15-20%
Match trailing distance to position duration.
Crypto-Specific Considerations
Cryptocurrency exhibits much higher volatility. Bitcoin routinely moves 5-8% daily. Altcoins swing wider.
My crypto distances start at 15% minimum. Often use 18-20% for smaller altcoins. These prevent noise-triggered exits.
The 24/7 nature makes trailing stops especially valuable. They protect during sleep and weekends.
Start wider than comfortable. Track results over 20-30 trades. Tighten if leaving too much on table. Widen if choppy markets trigger repeatedly.
What Is Stop Loss In Share Market: Implementation Across Different Markets
Trailing stops function similarly across markets. But specific considerations matter for each asset class.
Equity Markets
Overnight gaps pose primary risk. Earnings create sudden price jumps. Trailing stops can't protect during closed hours.
My approach: Widen stops before earnings. Consider exiting for major announcements. Gap risk increases during earnings season.
Market hours limitations require planning. Large-cap stocks support tighter trails. Small-caps need wider distances due to lower liquidity.
Cryptocurrency Markets
Crypto operates 24/7/365. Continuous protection tops the advantage list. Trailing stop watches market while you sleep.
Higher baseline volatility demands wider trails. I use 15-20% for crypto positions. Anything tighter gets stopped by normal movement.
Weekend volatility exceeds weekday movement often. Traditional markets close Friday. Crypto continues trading. Trailing stops protect automatically during these periods.
I maintain different parameters for each market. Equity positions: 8-12%. Crypto positions: 15-20%. This reflects volatility differences.
Strategic Applications of Trailing Stop Loss
Trailing stops shine in specific trading scenarios. Three applications dominate my approach.
 Trend Following
Trend Following
Trailing stops align perfectly with trend systems. Both capture extended directional moves.
I enter trending positions with risk-based stops. Once profit reaches 1.5x initial risk, activate trailing stops. This locks minimum gains.
The mechanism lets trends develop fully. Avoid premature exits during pullbacks. Stop adjusts upward with each new high.
Breakout Trading
Breakouts require immediate protection. Failed breakouts retrace quickly. Trailing stops provide automatic protection.
Initial stops sit just below breakout level. Once price extends 5-10% beyond breakout, switch to trailing mode.
Captures momentum runs while protecting against reversals. This combination produces excellent risk-reward.
Position Scaling
Trail half position with tighter stops. Other half gets wider parameters.
This locks guaranteed profits while letting winners run. Tighter stops secure base returns. Wider stops capture extended moves.
Recent example: 200 shares at $50. Trailed 100 with 8% stops. Remaining 100 at 15%. First half exited at $58. Second rode to $67.
Implementing Advanced Trailing Strategies with Professional Platforms
Sophisticated trading requires reliable infrastructure. Particularly in crypto markets where 24/7 execution matters.
Professional platforms like Upscale.trade provide the tools serious traders need. Their system executes trailing stops continuously without interruption. No sleep gaps. No weekend worries. Your risk management operates constantly.
The platform simplifies complex trailing strategies across multiple positions. Each position tracks independently with real-time adjustments. Execution quality remains consistently high even during volatile periods.
For traders managing positions across equity and crypto markets, professional infrastructure becomes essential. The reliability and advanced features justify themselves quickly through better execution and peace of mind.
Using Trailing Stops in Trending Markets
Strong trends create ideal conditions for trailing stops. Price moves consistently in one direction. Pullbacks remain shallow.
I identify trending conditions first. Look for higher highs and higher lows. Rising moving averages confirm trend.
My crypto trend example: Altcoin entered at $0.45 in early bull market. Set 18% trailing stop at $0.37.
Price rallied to $0.60 in two weeks. Stop moved to $0.49. Maintained 18% distance below peak.
Momentum continued. Token reached $0.85 at month three. Stop at $0.70. Guaranteed profit locked.
Trend extended to $1.10 before weakness. Final stop: $0.90. Exit triggered at $0.91.
Total gain: 102% from entry. Trailing captured 83% of entire trend. Fixed stop would have exited far earlier.
Crypto's 24/7 nature makes trailing stops particularly valuable. Captures extended moves without constant monitoring.
When to Use Trailing Stop Loss
Strategic selection between stop types significantly impacts results.
Optimal Scenarios for Trailing Stops
Strong trending markets top the list. When trend strength appears robust, activate trails immediately.
Uncertain profit targets favor trailing approaches. You believe in upside but can't predict the top. Let the market decide exit.
Passive position management suits trails perfectly. Can't monitor constantly. Automated adjustment handles management.
Larger positions demand profit protection. As positions grow profitable, trailing stops lock gains automatically.
When to Avoid Trailing Stops
Ranging choppy markets create problems. Price whipsaws trigger stops prematurely.
I experienced this. Eight consecutive ranging trades stopped out. All would've been profitable with fixed stops.
Defined profit targets suggest regular stops. You target specific levels. Fixed stops at predetermined exits make sense.
Very short-term trades don't need trailing complexity. Day trades use fixed stops. The adjustment adds complication.
High-impact news events require caution. Fed announcements, earnings, protocol updates create spikes. Fixed stops often prove safer.
Low liquidity instruments pose execution risks. Small-cap altcoins with wide spreads can't support tight trails. Use wider fixed stops instead.
Adjusting Trailing Stops for Volatile Markets
Market volatility fluctuates constantly. Your strategy must adapt accordingly.
I measure volatility daily using ATR indicator. When ATR exceeds 14-day average by 50%+, adjustment triggers.
Volatility Response System:
- Calculate current ATR value
- Compare to recent average
- Widen trails proportionally if elevated
- Monitor support/resistance levels
- Adjust review frequency
During volatile periods, review daily instead of weekly.
Real example: Tech stock showed ATR of $3. Volatility spike pushed it to $7. I widened 8% trail to 15% immediately.
Wider stop avoided three premature triggers. Final exit at 22% gain. Tight trail would've stopped at just 4%.
Crypto Volatility Baseline
Crypto exhibits permanently higher volatility. Bitcoin commonly moves 5-8% daily. Altcoins swing 10-20%.
I start at 15% for BTC positions. Altcoins get 18-22% trails. These accommodate normal crypto movement.
Don't apply equity parameters to crypto. Different volatility regimes demand different approaches.
Common Trailing Stop Loss Mistakes and How I Avoid Them
Learning from errors accelerated my progress. These mistakes cost me significantly.
Mistake 1: Trailing Distance Too Tight
Used 5% trails on volatile growth stocks. Normal movement triggered exits constantly.
Solution: Use ATR-based distances. Calculate 2-3x ATR value. Success rate improved immediately.
Mistake 2: Using Trails in Ranging Markets
Applied trails during consolidation. Lost eight consecutive trades.
Solution: Identify market regime first. Only use during trending conditions. Win rate jumped 15%.
Mistake 3: Ignoring Gap Risk
Held positions through earnings with active trails. Overnight gaps blew through stops.
Solution: Widen stops before catalysts. Better yet, close positions. Gap risk exceeds reward often.
Mistake 4: Moving Stops Against Position
Manually moved stop lower to avoid exit. Position continued falling. Large loss resulted.
Solution: Never loosen trailing stop once set. Discipline proves essential.
Mistake 5: Applying Equity Parameters to Crypto
Used 8% equity trails on crypto. Stopped out within hours. Bitcoin's volatility exceeded stop distance.
Advanced Trailing Stop Loss Techniques
Professional traders enhance basic trailing stops with refinements. These techniques deliver superior results.
Volatility-Adjusted Dynamic Trails
Advanced approach adjusts distance based on real-time volatility changes.
My system: Normal ATR = 10% trail. ATR increases 50% = widens to 15%. ATR decreases 30% = tightens to 8%.
Results: Premature stop-outs decreased 40%. Average winner size increased 18%.
Partial Position Trailing
Split position into components with different parameters.
My allocation: 50% with 8% trail (tighter). Remaining 50% with 15% trail (wider).
Example: 200 shares at $50. First 100 exit at $58. Second 100 exit at $67. Blended return: 30%.
The split outperforms single method consistently.
Time-Based Trail Tightening
Distance narrows as position ages:
- Day 1-7: 15% trail
- Day 8-21: 12% trail
- Day 22+: 9% trail
This recognizes decreasing trend continuation probability over time.
Combining Trailing Stops with Technical Indicators
Technical analysis enhances effectiveness dramatically.
Moving Average Trails
Use 20-day EMA as a dynamic stop level. Price above EMA = hold. Price below EMA = exit immediately.
This works beautifully in strong trends. Captured 67% gain in tech stock. EMA trail prevented premature exit.
ATR-Based Distance
Set distance at 2-3x current ATR value. Recalculate weekly. Adjust accordingly.
This reduces premature stop-outs by 35%. Respects market character naturally.
Support/Resistance Alignment
Place trails just below key support levels. Support holds during pullbacks. Break suggests genuine reversal.
Trailing Stop Loss with Book Profit
Combining trailing stops with profit targets creates powerful hybrid strategies.
OCO Order Implementation
One-Cancels-the-Other orders execute either trailing stop or profit target. Whichever triggers first closes position.
Setup: Enter position. Set profit target at resistance or 2:1 risk-reward. Activate trailing stop at wider distance. Link both as OCO order.
Example: Bought at $100. Profit target at $120. Trailing stop 15% at $85.
Price rallied to $118 but reversed. Trailing adjusted to $100 during move. Exited at $101 on reversal.
Result: Small profit instead of loss. Hybrid provided downside protection while chasing upside.
Use when trend direction uncertain but setup strong. HDFC Securities and major platforms support OCO functionality.
What Is Stop-Loss With Example: Practical Applications
Real case studies demonstrate trailing stops better than theory.
Case Study 1: Trending Market Success
Technology stock entered at $85. Initial stop $78 (8% risk).
Activated 10% trailing at $95 when profit exceeded 1.5x risk.
Trail adjustments:
- Day 7: $98 → Stop $88.20
- Day 14: $106 → Stop $95.40
- Day 21: $115 → Stop $103.50
Exit at $107.50 when triggered.
Final result: $22.50 gain (26.5% return). Trail captured 66% of total move.
Case Study 2: Crypto Volatile Market
Ethereum entered at $2,000. Initial 18% trail (crypto baseline).
Day 8: Volatility spike doubled ATR. Widened trail to 22%.
Trail adjustments:
- Day 10: $2,400 → Stop $1,872
- Day 15: $2,800 → Stop $2,184
- Day 21: $3,100 → Stop $2,418
Exit at $2,320.
Result: $320 gain (16% return). Original 18% trail would've stopped out prematurely at $2,050. The volatility adjustment prevented early exit.
Case Study 3: Partial Position Strategy
Growth stock at $50. Split 200 shares.
Position 1: 100 shares with 8% trail (tighter) Position 2: 100 shares with 15% trail (wider)
Exit results:
- Position 1: Triggered at $59 (18% gain)
- Position 2: Triggered at $58 (16% gain)
Blended return: 17% overall. Split balanced aggressive taking with trend-riding patience.
Conclusion
Trailing stop loss orders transform risk management fundamentally. They protect capital while letting profits run.
Key principles:
Trailing stops excel in trending markets. Ranging conditions need different approaches. Match tools to market regime.
Proper distance setting proves critical. Use volatility-based methods. Adjust for different markets. Crypto needs wider trails than equities.
Platform implementation matters. Test on small positions first. Verify execution quality before increasing size.
Combine trails with complementary tools. Technical indicators enhance performance. Build comprehensive systems.
Systematic rules prevent emotional mistakes. Never loosen trailing stops manually. Document parameters clearly.
Start with basic percentage trails. Gain confidence through practice. Progress to advanced techniques gradually.
My philosophy: Trailing stops form one component of complete risk management. Used skillfully, they dramatically improve outcomes.
Implementation Checklist:
- Define market regime
- Calculate appropriate distance
- Select trail type
- Set up platform orders
- Document parameters
- Monitor execution
- Review and adjust
Begin with one position. Apply trailing stop. Observe how it functions. Expand usage gradually.
Master trailing stops and your trading transforms permanently. Test approaches on demo accounts first. Build confidence before risking capital.
FAQ
1. What is a trailing stop loss?
A trailing stop loss is a dynamic order type that automatically adjusts your exit price as the market moves favorably. Unlike regular stop losses that remain fixed, trailing stops follow price movements upward, locking in profits while providing downside protection.
2. How does a trailing stop loss work?
You set a trailing distance (percentage or dollar amount) below the current market price. As price moves up, your stop adjusts upward by that distance. The stop never moves down. When price reverses and hits the trailing stop level, the position closes automatically.
3. How is a trailing stop loss different from a regular stop loss?
Regular stop losses stay at a fixed price level. Trailing stop losses adjust automatically with favorable price movement. Regular stops only limit losses. Trailing stops both limit losses and protect accumulated profits.
4. What are the advantages of trailing stop loss?
Key advantages include: automatic profit protection, emotion-free exits, ability to capture extended trends, hands-off position management, and systematic risk control. They work especially well in trending markets and for traders who cannot monitor positions constantly.
5. What are the disadvantages of trailing stop loss?
Main disadvantages: premature exits in choppy markets, vulnerability to volatility spikes, more complex setup than regular stops, and potential for whipsaw losses in ranging conditions. They perform poorly in sideways markets and during high-impact news events.
